Melanoma Classification
By Heba Mohamed
- 3 minutes readTable of Content
Abstract
Skin cancer is the out-of-control growth of irregular skin cells causing the skin to rapidly multiply and form malignant tumors. Between 2008 and 2019 the number of new invasive Melanoma cases rapidly increased by 54%. With such a substantial escalation, it is of great importance for us to inaugurate and build on techniques to assist healthcare providers in diagnosing skin cancer at its preliminary stages.
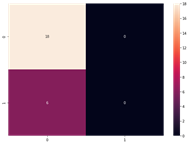
I developed a classification model for classifying the images to Melanoma or not motivated by the performance of Convolutional Neural Networks in computer vision, I present a CNN-based model from scratch. The results show that the system performs a training accuracy of 97.5% and testing accuracy 75%. In the testing stage the model predicted 18 images correctly, as it classified them from the Nevus type (class 0), and they are, but it failed to predict 6 images from the Melanoma (class 1).
Propblem Statements
Skin cancer is the out-of-control growth of irregular skin cells causing the skin to rapidly multiply and form malignant tumors. Between 2008 and 2019 the number of new invasive Melanoma cases rapidly increased by 54%. With such a substantial escalation, it is of great importance for us to inaugurate and build on techniques to assist healthcare providers in diagnosing skin cancer at its preliminary stages.
Melanoma is one of the most aggressive types of skin cancer as it rapidly spreads to various areas of the body. With the increase and fatal nature of melanoma, it is of utmost importance to establish computer-assisted diagnostic support systems to aid physicians in diagnosing skin cancer.
Dataset
The PH² dataset has been developed for research and benchmarking purposes, in order to facilitate comparative studies on both segmentation and classification algorithms of dermoscopic images. PH² is a dermoscopic image database acquired at the Dermatology Service of Hospital Pedro Hispano, Matosinhos, Portugal.
The dermoscopic images were obtained at the Dermatology Service of Hospital Pedro Hispano (Matosinhos, Portugal) under the same conditions through the Tuebinger Mole Analyzer system using a magnification of 20x. They are 8-bit RGB color images with a resolution of 768x560 pixels. This image database contains a total of 200 dermoscopic images of melanocytic lesions, including 80 common nevi, 80 atypical nevi, and 40 melanomas. The PH² database includes medical annotation of all the images namely medical segmentation of the lesion, clinical and histological diagnosis, and the assessment of several dermoscopic criteria (colors; pigment network; dots/globules; streaks; regression areas; blue-whitish veil).
Proposed Solution
I wanted to explore data science-related jobs posted to a variety of cities on indeed.com, a job aggregator that updates multiple times daily. I conducted my scraping using the “requests” and “BeautifulSoup” libraries in python to gather and parse information from indeed’s pages, before using the “pandas” library to assemble my data into a dataframe for further cleaning and analysis.
Tools
- Python 3.
- Pandas Library.
- NumPy Library.
- matplotlib Library.
- OpenCV Library.
- Sklearn Library.
- Keras APIs.
- Local Jupter Notebook.
- Microsoft Word.
Prject Stages
Model Architecture
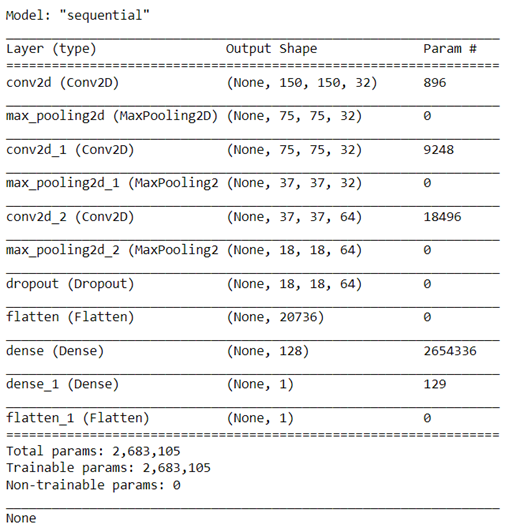
Model Training
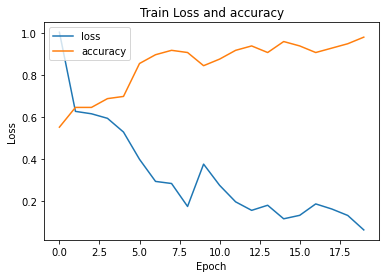
Training loss and accuracy graph
Model Testing
Using the predict_generator function on 24 testing images we got these results.
- Y Actual = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0]
- Y prediction = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
Model Evaluation Metrics
- Accuracy score = 75%
- Precision score = 75%
- Recall score = 75%
- F1 score = 75%
- Confusion Matrix.
More Resources
- For more details see the project repository on github.
- Dispaly the project detailed report from here
- Dataset